
The type of glycosidic bond is very important because enzymes distinguish it very strictly. As the hemiacetal hydroxyl group of a saccharide condenses with another monosaccharide, a homoglycoside (glycan) of the α- and β-glycoside type is formed. alcohol, phenol, sterols, terpenic alcohols, hydroxy derivatives of heterocycles) and heteroglycosides are formed.
#Non reducing anomeric carbon free#
Many carbohydrates do not occur free in nature, but the hemiacetal hydroxyl group can be replaced by an organic component (e.g. on the C1 carbon of aldoses and the C2 carbon of ketoses), forming so-called glycosides, and their bond is called a glycosidic bond. During the oxidation of ketoses, the carbon of the oxo group becomes asymmetric, which is why a mixture of two alcoholic sugars differing in the position of the hydrogen and the –OH group on this carbon is formed (D-glucitol and D-mannitol are formed from D-fructose).Ĭarbohydrate derivates Ī special group of monosaccharide ethers consists of ethers that are formed by esterification to hemiacetal hydroxyl group (i.e. Their names are formed by adding the ending -tol to the root of the name of the corresponding aldose. L-ascorbic acid (L-gulonic ketocarboxylic acid dehydrolactone, vitamin C) can be oxidized to biologically inactive dehydroascorbic acid.Ĭarbohydrate reduction Īldoses and ketoses can also be enzymatically reduced to polyhydroxyalcohols, the so-called alcoholic sugars - alditols, by the action of mild reducing conditions. Ketoses under the action of strong oxidizing agents give hydroxydicarboxylic acids with a smaller number of carbons, because the carbon chain between the first carbon and the carbon of the keto group is split. Of the mentioned oxidation products of monosaccharides, the ability to form hemiacetals is therefore preserved only in the case of uronic acids. glucaric acid) are formed by simultaneous oxidation of the aldehyde group and the primary alcohol group.īy oxidizing the aldehyde group to a carboxyl group, the newly formed compound loses its ability to form cyclic (semi-acetal) forms. Reduction of glucuronic acid produces gulonic acid, which provides gulonolactone, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid. Starch in plants and glycogen in animals serve as storage substances.Ĭarbohydrate structure Īscorbic acid ( vitamin C ) is an α-lactone, synthesized by plants and most animals (except primates and guinea pigs). cellulose, chitin), where they fulfill a supporting function. They are also a basic component of the cell walls of plants and bacteria (e.g.
Humans can synthesize carbohydrates (with the exception of vitamin C) mainly from amino acids.They play an important role in internal and intercellular communication and immunity.They form the structural elements of the membranes of lower organisms and in the form of complex liposaccharides and glykoproteins or proteoglycans are part of membranes and tissues of animals and humans.They are part of nucleotides, RNA a DNA.Carbohydrates are metabolic intermediates for synthetic processes.

Carbohydrates are an important and fastest source of energy.9.2 Used literature: Lekárska biochémia, Dušan Dobrota a kolektívīiomedical significance.7.3.2 Synthesis, transport and function of glykoproteins.
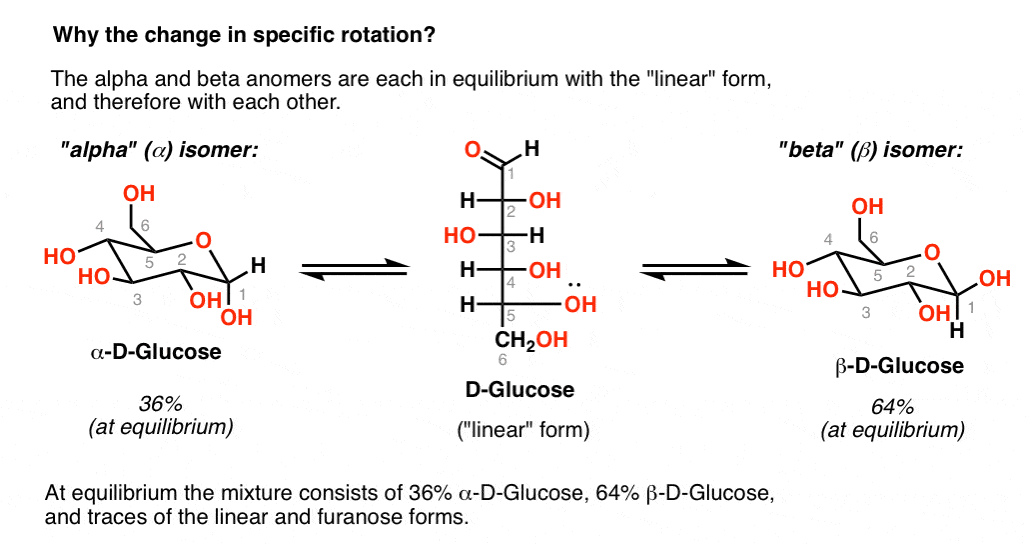


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
